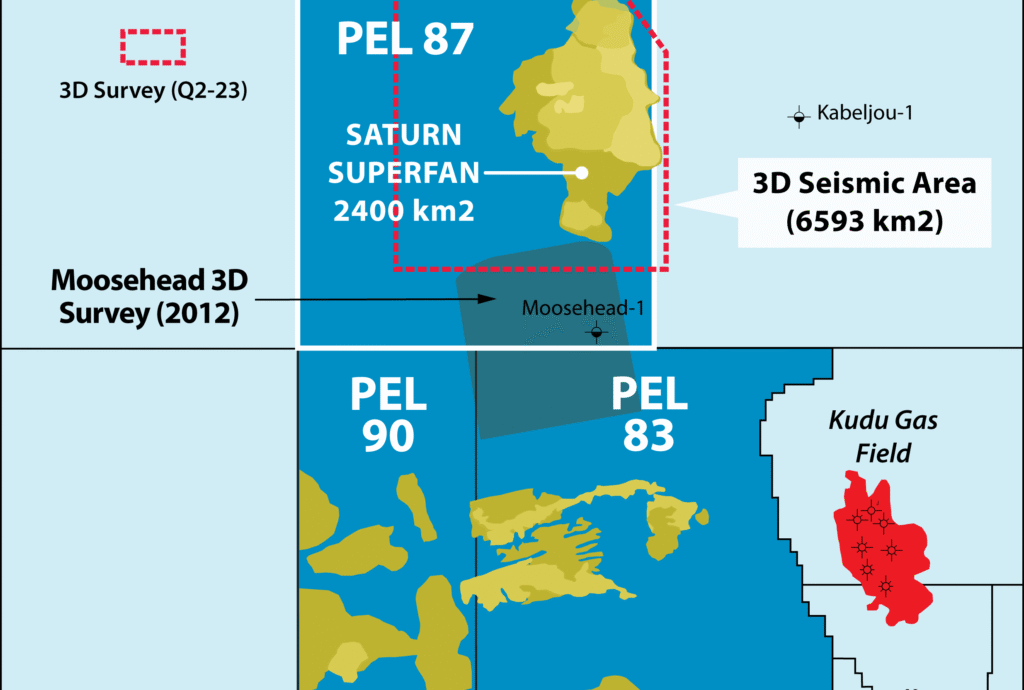
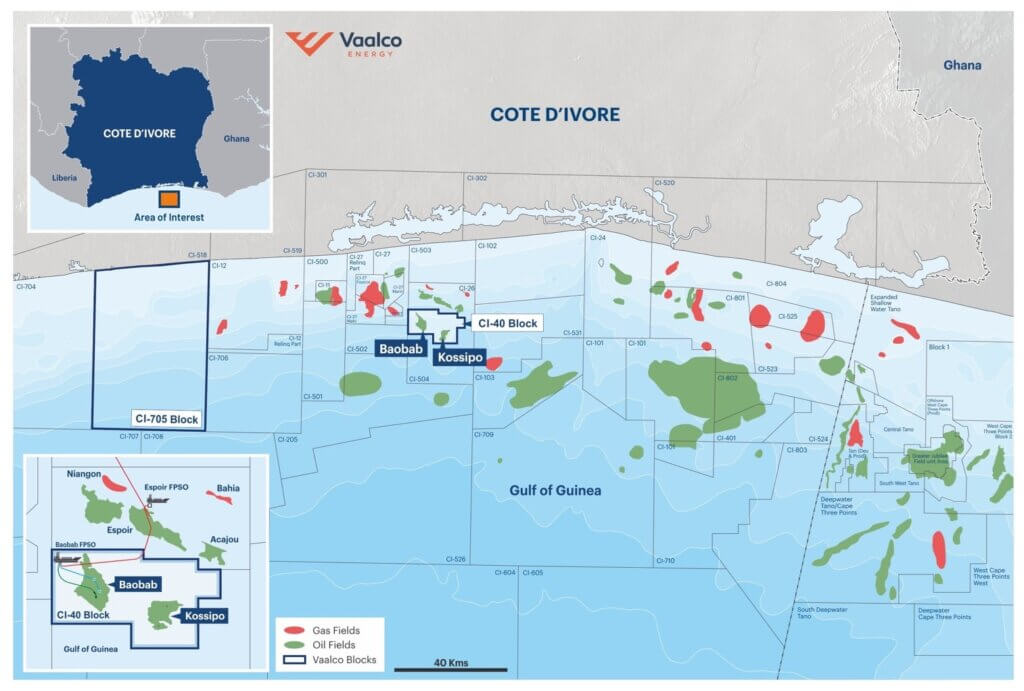
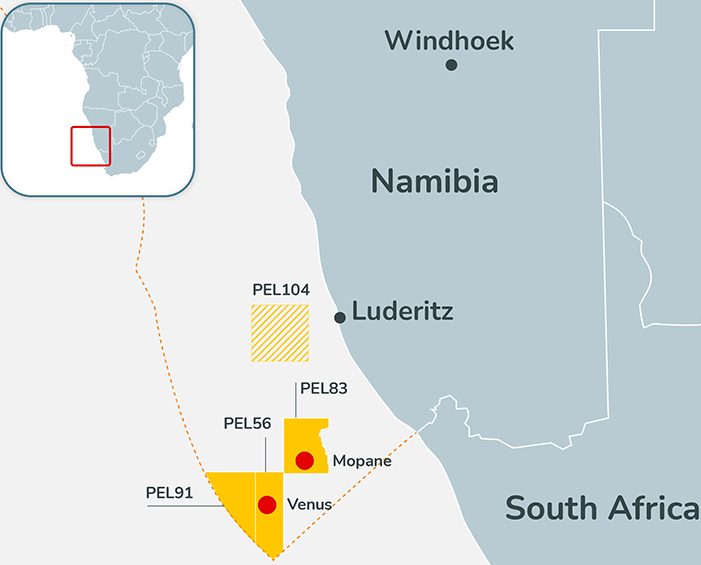
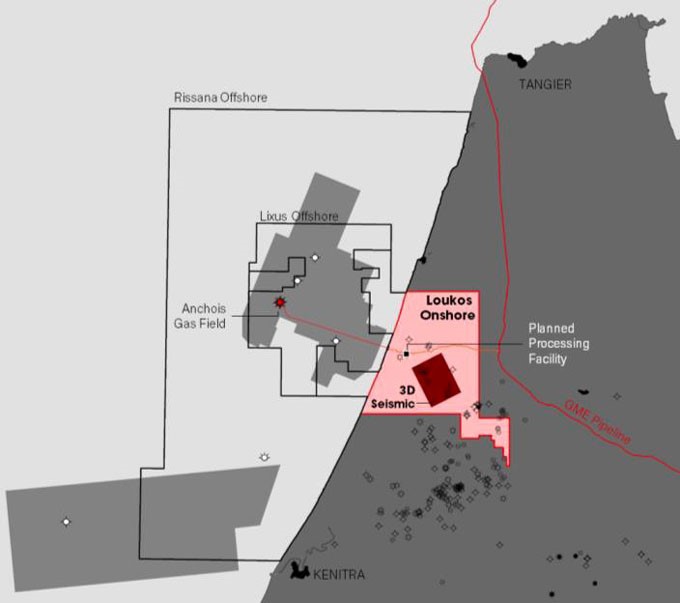
Africa stands at a crossroads in the flow of global energy dynamics — a pivotal moment where the continent can leverage its abundant fossil fuel resources for equitable development. To ensure this outcome, stakeholders must concentrate investment on key areas like refining capacity, trading networks, and adoption of cleaner fuels if Africa is to be prepared for the 2050 projections covered in the African Energy Chamber’s (AEC) 2026 Outlook Report, “The State of African Energy.”
Africa’s need for refined products is set to surge, driven by demographic and economic forces. According to our report, Africa’s refined product demand is projected to climb from approximately 4 million barrels per day (bbl/d) in 2024 to over 6 million bbl/d by 2050.
While many advanced economies are moving to reduce their dependence on oil and gas, Africa is next in line to benefit from its own — and has every right to do so, just as the developed nations of the world already have. This situation highlights both the opportunities for energy security and the challenges that lie ahead regarding infrastructure development.
A Unique Trajectory
While many other regions around the world are expected to follow the same path toward green alternatives as Europe and North America in the coming years, Africa’s oil demand shows no sign of waning anytime soon. However, Africa’s trajectory is markedly different: Per capita consumption remains the lowest globally, particularly in sub-Saharan African nations, leaving substantial room for expansion as populations and GDPs rise.
Forecasts suggest that the continent’s population could swell by more than 930 million people, reaching nearly 2.4 billion by 2050. This would account for 25% of the world’s population and 63% of global population growth between now and then.
Economic projections are equally substantial, with Africa’s 2050 GDP expected to nearly triple from what it is now to around USD7.8 trillion after growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8-3.9% in the coming decades. Smaller, less developed markets will lead this charge, amplifying demand for energy-intensive activities.
Currently, despite representing 18% of the global population, Africa consumes less than 5% of the world’s oil products and contributes just 3% to global GDP.
This disparity indicates untapped potential.
As the 2026 Outlook Report emphasizes, Africa’s oil demand will continue growing to 2050 and beyond, fueled by population growth, industrialization, and urbanization. Furthermore, while sub-Saharan Africa’s per capita oil demand is the world’s lowest, there is a dire need for an increased supply of oil and gas products, positioning the region as an engine for long-term growth.
Gasoline: Global Growth Will Be African
Africa is poised to become the primary driver of worldwide gasoline demand growth over the long term, offsetting declines in China and member countries of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Our report projects that Africa’s gasoline consumption will exceed 2.2 million bbl/d by 2050, with Nigeria and emerging markets at the forefront.
Nigeria already dominates continental gasoline demand, yet its per capita usage is still comparatively low. In established markets like Algeria, Morocco, Egypt, and South Africa, demand is expected to stagnate in the early 2040s due to overall improving fuel economy, the rise of compressed natural gas (CNG)/liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) vehicles in Egypt and Algeria, and electric vehicle (EV) adoption in South Africa.
The spotlight on the transportation sector in our 2026 Outlook Report reveals that the continent’s overall gasoline needs will still rise over the next 25 years as the prevalence of gasoline-powered light-duty vehicle fleets is not expected to wane. Though alternative powertrains like EVs will penetrate the market, they’ll do so slowly due to the inadequate electricity supply and the scarcity of a charging infrastructure. Therefore, gasoline will remain the backbone of personal and commercial mobility, especially in the less developed regions where economic activity requires road transport.
Diesel/Gasoil: Fueling Industrial and Extractive Expansion
Diesel/gasoil will see even more pronounced growth, with consumption expected to increase by about 880,000 bbl/d by 2050, nearly 50% from current levels, and growing to just under 2.7 million bbl/d. This positions Africa as the top growth region for the product, surpassing Latin America.
Beyond road transport, demand will be propelled by the extractive industries. Investments in critical minerals that support energy transition (e.g., lithium, cobalt, and nickel) are accelerating in mineral-rich Central and Southern Africa. Much of the growth in demand for diesel/gasoil will come from countries like Angola, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Development in the Copperbelt region between Zambia and the DRC, with initiatives like the Lobito Corridor project, will intensify diesel needs for mining operations and power generation.
Private and commercial trucking will further contribute, as population and GDP growth will necessitate an increase in the transportation of goods in general. Unlike gasoline, diesel’s versatility in heavy-duty applications will ensure a sustained demand, even as cleaner alternatives emerge in other sectors.
Aviation Fuels: Recovery and Long-Term Ascent
Jet fuel and kerosene demand is on the verge of a strong rebound in Africa with expectations that it will surpass its pre-COVID levels in 2025. Inter- and intra-regional air travel is regaining momentum, with consumption projected to top 280,000 bbl/d this year and increase 65% by 2050, reaching a rate of 465,000 bbl/d.
Along with population expansion, this growth will stem from tourism, business travel, the gradual growth of an urban middle class, and infrastructure investments. Projects like Ethiopia’s new airport southeast of Addis Ababa and the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) will enhance connectivity, increasing passenger air travel and freight transport.
A Cleaner Cooking Solution with Untapped Potential
Amid rising demand for refined products, LPG as a cooking fuel is the standout opportunity for cleaner energy. Our 2026 Outlook Report identifies LPG as the most abundant and practical alternative to traditional biomass and coal for African households as it offers health and environmental benefits as well as a means of reducing emissions.
Today, over 900 million Africans lack access to clean cooking solutions, relying on wood, dung, coal, or paraffin — fuels that cause toxic indoor pollution, deforestation, and high greenhouse gas emissions. The switch to LPG would reduce particulate matter by 98% and save 1.2 million hectares of forest annually (a quarter of global deforestation). More importantly, this would also reduce the number of deaths and the prevalence of the devastating health conditions that these particulates cause. The conversion to LPG cooking would also cut black carbon emissions by 117 million tonnes of CO2 equivalent each year. Overall, CO2 reductions could reach 279 million tonnes per year, an amount comparable to the total emissions of mid-sized nations like Taiwan or Malaysia.
Despite these advantages, LPG use remains low at under 20 million tonnes per year. Our report, based on S&P Global Commodity Insights data as of June 2025, predicts only modest growth, with Nigeria, Morocco, Egypt, South Africa, Algeria, and others contributing to a slight rise as we head toward 2050.
Barriers and Pathways Forward
The modest projections in our report can be attributed to persistent policy and infrastructure hurdles. Regulatory frameworks, consumer financing plans, and distribution networks in rural and low-income areas would all need development. Without targeted investments, demand will remain suppressed.
The upside potential is significant, however. Countries like Kenya, Nigeria, and Côte d’Ivoire demonstrate that, with supportive policies, LPG adoption can accelerate. As our report suggests, if the latent demand for LPG were unleashed, projected consumption in 2050 could more than double from current forecasts.
Africa’s surge in demand for refined products is a multifaceted issue that will require proactive planning. Over USD20 billion in downstream infrastructure investment is needed by 2050 to handle imports and distribution. Flagship projects like Nigeria’s Dangote refinery are vital but insufficient on their own, and the smaller initiatives we are seeing in Angola and Uganda won’t bridge the gap.
As our 2026 Outlook Report illustrates, Africa’s energy future is one of tremendous growth. To ensure that this future will be prosperous and support the growing needs of all Africans, policymakers, investors, and international partners must prioritize efficient trading, local refining, and a transition to fuels like LPG to maximize value for the continent’s 2.4 billion people by mid-century.